Times are fast changing, and with them, telecommunications requirements for high-grade and high-speed data transmission have never been higher. As coaxial cable infrastructures reach their limits concerning bandwidth and signal quality, new technologies have been developed to bridge the capabilities of optical fiber with existing coaxial systems, among them RF over Glass.
Understanding RfoG
The RF Over Glass technology leverages the best of both worlds utilizing the strengths of the fiber optics while using their coaxial cable infrastructures in place. In a nutshell, it will enable the cable operator to send RF onto the fiber optic network for seamless integration of high-speed internet, video, and data services.
How RFoG Works
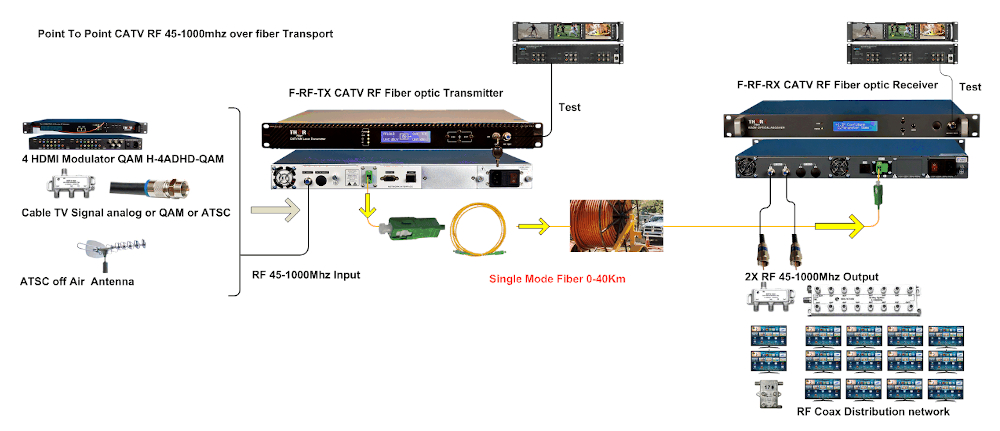
RFoG works by converting the RF signals into their optical form, which is transmitted on fiber optic cables. How this is done follows.
Transmission: The Fiber Optic Transmitter changes RF signals from coaxial cable into optical. That way, the signals can be transmitted without any significant loss in strength over a long distance. It is an optical fiber transmission wherein these converted optical signals travel via fiber optic cables that are immune to electromagnetic interference and can hence carry voluminous data over long distances.
Receiving: At the far end, an optical receiver converts it into RF for distribution over coax. This allows the use of the existing cable infrastructure without needing an overhaul of the same.
Advantages of RFoG Technology
Higher Bandwidth: The major and one of the most key advantages of RFoG is its superior bandwidth. Fiber optic cables can support much higher data rates when compared to coaxial cables, making them highly potent in handling multiple services, including HD and UHD video, internet access, and voice services-all within a single infrastructure.
Smarter Quality of Signal: The quality of the signal is much better compared to what is obtained through the use of coaxial cable. The fiber optic technology is not prone to electromagnetic interference that normally interferes with the quality of the signal carried along coaxial cables. This therefore ensures sharper signals in audio and video; thus, the RFoG is very ideal for CATV over fiber applications.
Cost-Effectiveness: That's where RFoG saves the day: with an initial investment more costly in fiber optic infrastructure, RFoG allows the cable operators to recycle existing coaxial networks, reducing the overall cost of transitioning to fiber. This transition process can be done with much less aggravation and, therefore, at lesser cost using coax-to-fiber converters and other integration technologies for longer-term operations.
Future-Proofing: The nature of the telecommunications industry is one of fast change, and RFoG technology lends itself particularly well for adaptation in light of such emerging changes. From simple scalability to offering higher speeds and more services, RFoG systems are future-proof since they enable a cable operator to meet customer needs for many years to come. It has been quite a debate as to fiber vs coax; however, when considering the use of the technology of RFoG, it is critical to understand some of the differences. More data carriage and transmission can thus be realized to provide quality services.
Interference: Fiber optics are immune to electromagnetic interference. This is not the case with coaxial cables. This affects their performance, especially in RF venues where several signals are put to work.
Fiber Optic vs Coaxial Cable
In consideration of such a demand for high-quality data, fiber optics is usually considered to be superior in today's telecommunication. However, the technology of RFoG gives cable operators the potential to take advantage of the strengths in fiber optics without having to altogether discard coaxial infrastructures.
Practical Uses of RFoG Technology
RFoG technology is used in a number of different industries; a few are discussed below. RFoG enables the cable operator to provision high-value television services-including HD and UVD-on the same coaxial networks using fiber optics as backhaul.
Broadband Internet: RFoG systems make use of the high bandwidth in fiber optics to provide access to the Internet at higher speeds and hence fulfill the increasing demand for data by subscribers.
Telecommunication: RFoG technology will find application in a number of telecommunications applications by offering reliable and quality means of communications.
RFoG, in a sense, is the next quantum leap in the realm of cable TV networks, marrying the best of fiber optics with infrastructures currently in place based on coaxial cables. Increasing bandwidth, enhancing signal quality, and offering a less expensive route to future-proofing telecommunications systems, RFoG is well-poised to form a critical part of the evolutionary path for cable services. In the future, RFoG technology will be even more important to those cable operators who want to remain relevant to meet the high-quality demands of audio and video, let alone faster internet speeds. Understanding what RFoG can do, together with the advantages of fiber-optic systems, has the capability to let businesses and consumers alike make smart choices about their telecommunication infrastructures. RFoG stands out in the growing debate of fiber vs coax, proof that traditional and modern technologies can come together for the betterment of mankind with a connected future.

 ES
ES



