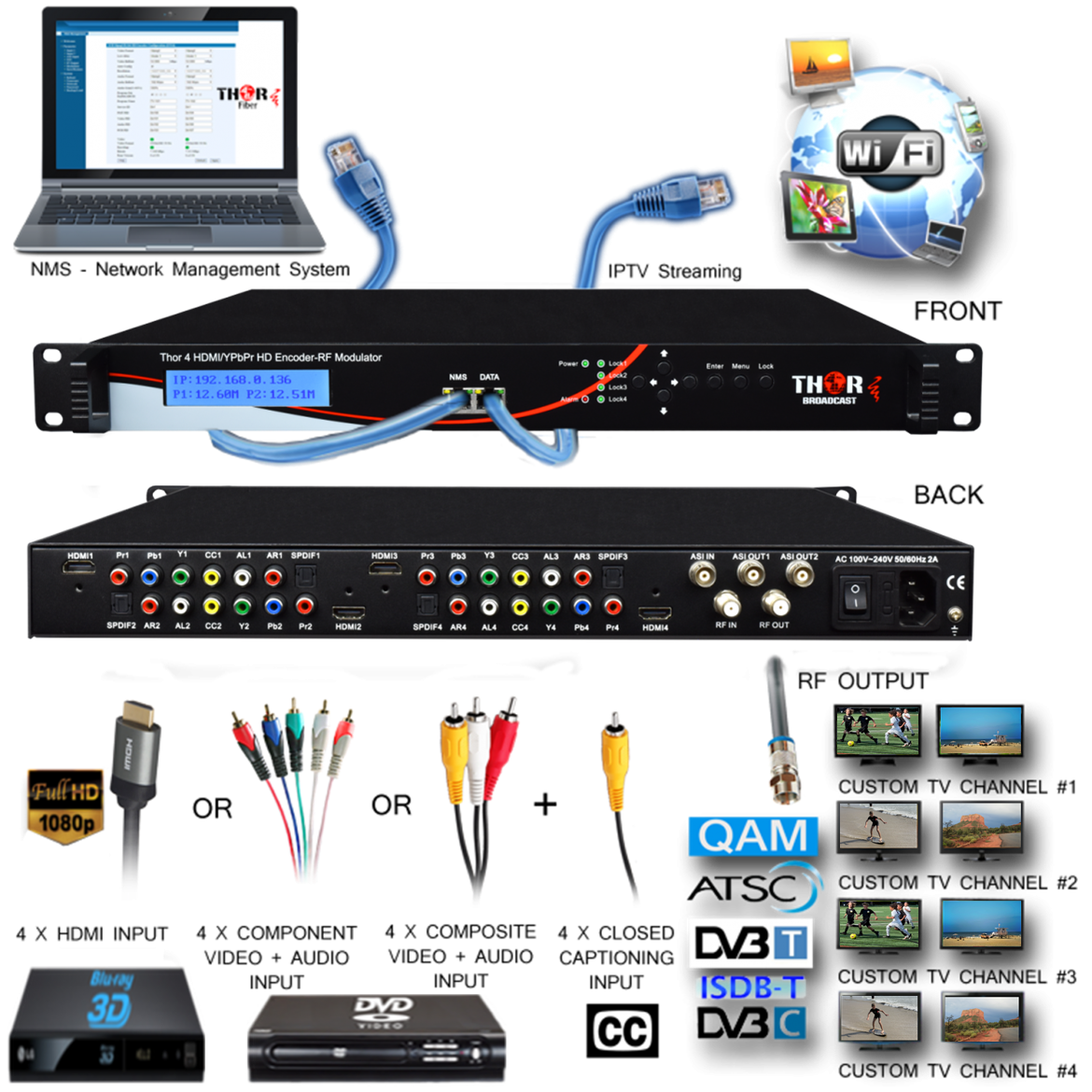
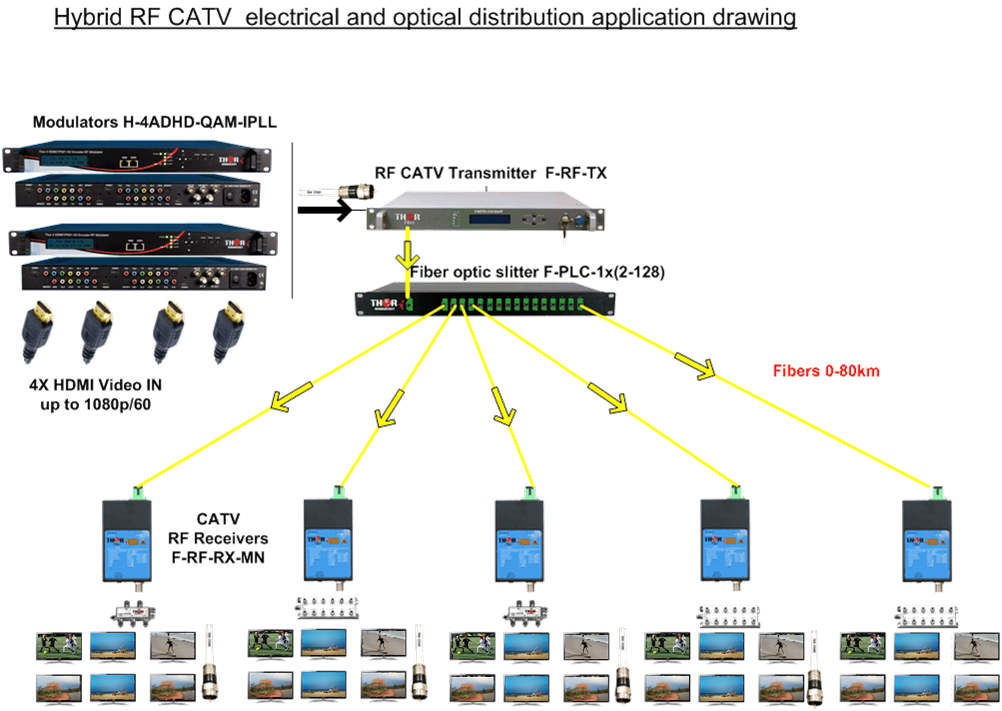
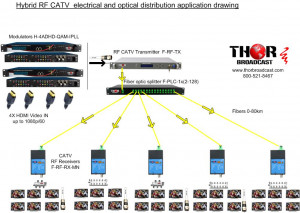
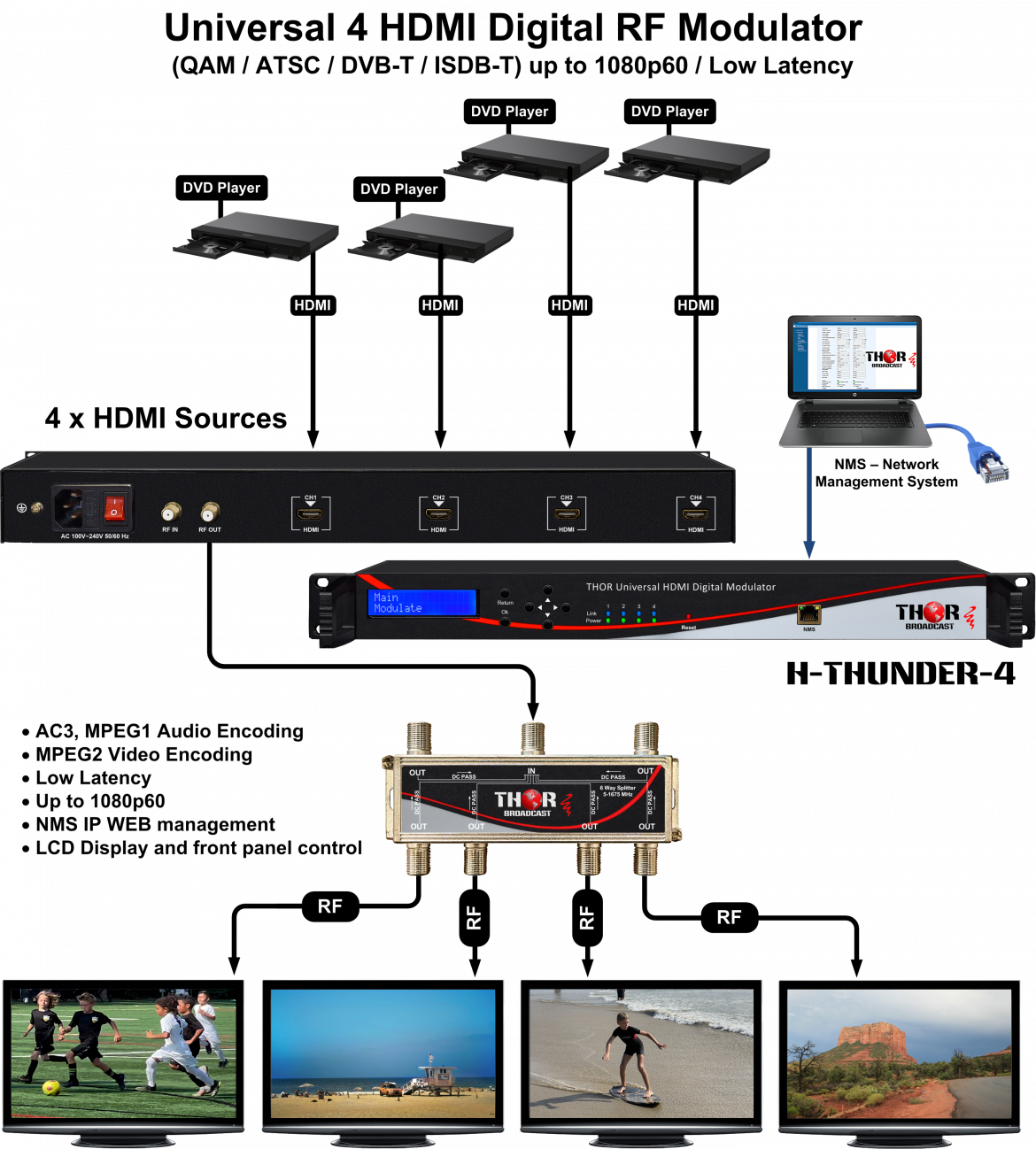
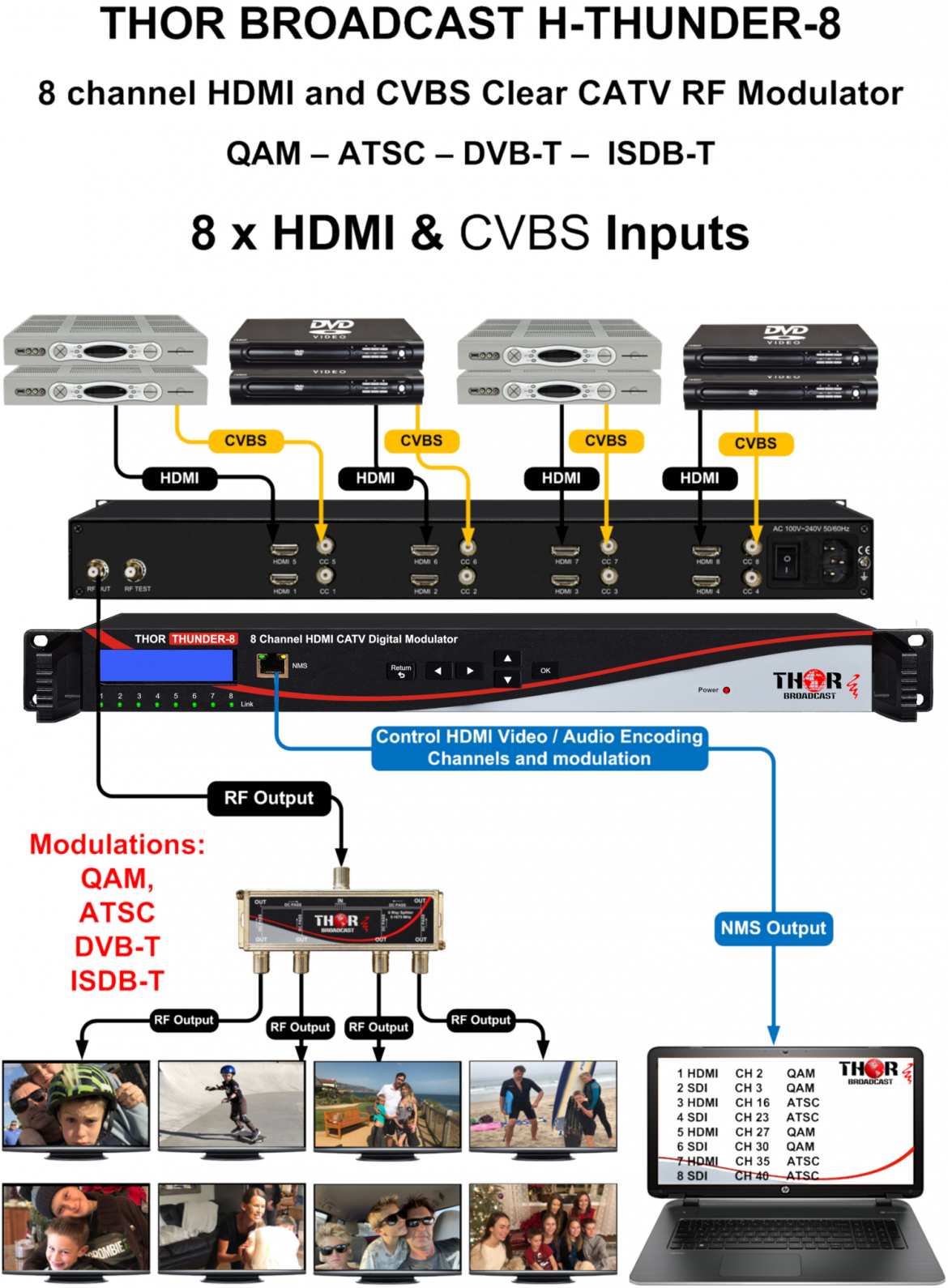
Answer: es, that model has an RF input and an RF output.
To your point it sounds like you'd want to combine the 4 HDMI inputs from various HDMI sources and add them to the existing channels from an Antenna.
You can input the RF from the Antenna into the RF input on the Modulator. You can also use an External 2x1 Comiber, it's the same thing essentially.
However you have to make sure the channels you assign the 4 HDMI inputs are not overlapping channels from the Antenna.
In order to properly assimilate the 2 RF streams together, they must be on vacant frequencies. Putting those HDMI sources on existing channels will not work.
The easiest way to do that is with an RF scanner, or just check online in your city which frequencies are vacant.
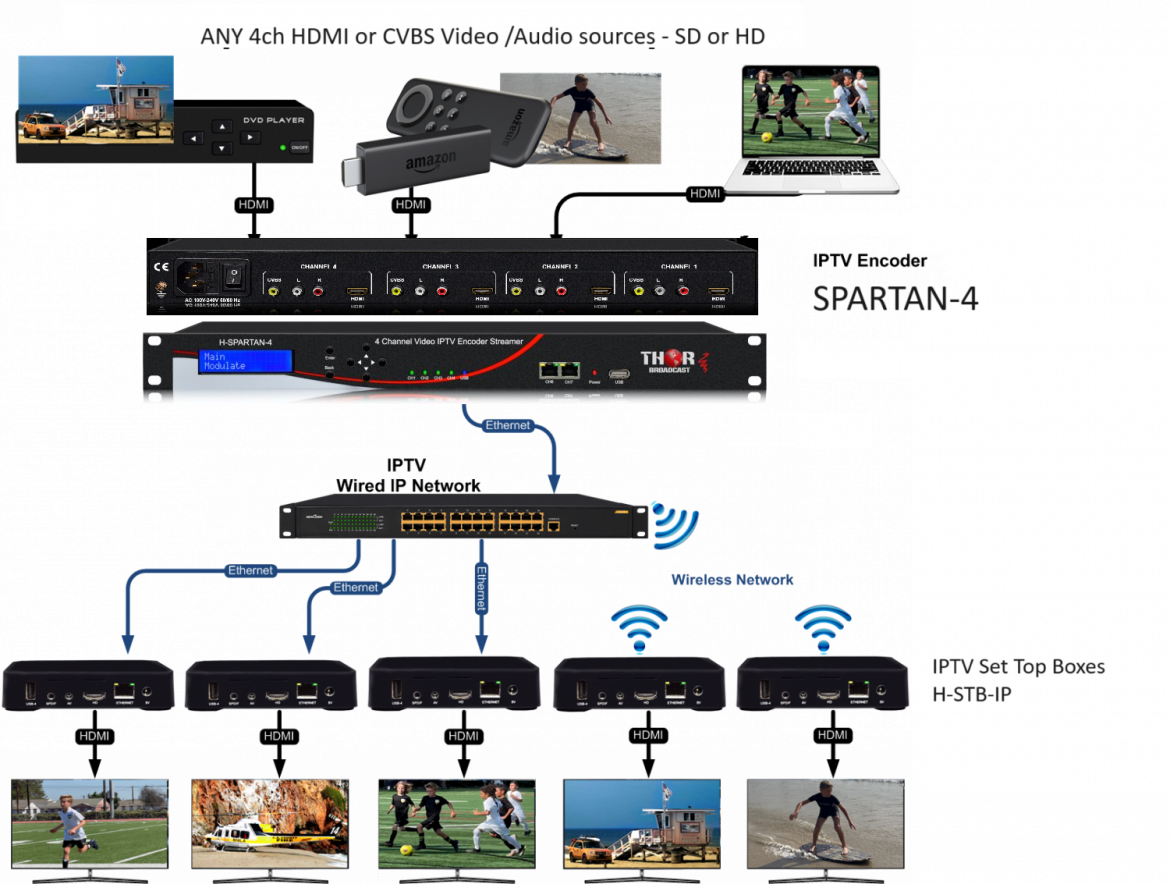
As for inputting RF antenna and expecting the model to output the antenna channels in IP is something it will not do. The only IPTV stream outputs would be from the 4 HDMI sources you are feeding the system.
So if you feed it 4 BluRay Players, then you can have 4 RTP/UDP/RTSP streams in multicast or unicast.
If you are looking to convert RF channels from an Antenna and converting them to IP channels or streams, then we have a different product for that called a Gateway.
This is our most dense RF Gateway, which can take up to 16 ATSC frequencies, Major and Minor channels, and convert them to IP streams.
We also have this available in an 8 RF channel input model.
Yes, you can connect both the Gateway and the Encoder to the switch; it needs to be a smart switch with the IGMP protocol enabled.
The IGMP works in a way that it keeps the streams in the switch's memory and passes the individual streams to the specific port where the stream was requested by any IP receiver or decoder.
This is more detailed explanation how the IGMP works:
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a communication protocol used to manage the membership of Internet Protocol (IP) multicast groups. IGMP is used by IP hosts and adjacent multicast routers to establish multicast group memberships. It plays a crucial role in enabling efficient network resource usage, especially for services like multicast video streaming. Here’s a simplified explanation of how IGMP works with multicast video streams and how it helps preserve bandwidth while allowing video access to anyone on the LAN network:
Multicast Video Streaming
-
Multicast Streaming: Unlike unicast streaming, where a separate copy of the video stream is sent to each requester, multicast streaming sends only one copy of the video stream to the network, regardless of the number of requesters. This method significantly reduces bandwidth usage.
-
Group Membership: Devices that wish to receive a specific multicast video stream will join a multicast group. The multicast group has a specific IP address that represents all devices interested in receiving the video stream associated with that group.
How IGMP Works
-
Joining a Group: When a device on the LAN wants to start receiving a multicast stream, it sends an IGMP message indicating its desire to join a specific multicast group.
-
Multicast Router: The local router receives the IGMP join request. The router then knows that it should forward traffic for that multicast group to the network segment where the request originated.
-
Leaving a Group: If the device no longer wishes to receive the multicast stream, it sends an IGMP leave message. If there are no more interested receivers on the LAN, the router stops forwarding the multicast stream to that network segment.
-
Periodic Queries: Multicast routers periodically send IGMP queries to discover if there are still devices interested in the multicast group. If no devices respond with a desire to remain in the group, the router assumes there are no interested receivers and stops forwarding the stream to that segment.
Preserving Bandwidth
IGMP efficiently manages network resources by ensuring that multicast traffic is only sent to network segments with interested receivers. This way, the bandwidth is not wasted on sending video streams to parts of the network where no device is interested in them.
Access by Anyone on the LAN
- Open Access: Any device on the LAN can join a multicast group to start receiving the associated video stream, making multicast video streams accessible to anyone on the network who wishes to receive them.
- Dynamic Membership: Devices can join or leave a multicast group at any time, allowing for flexible and dynamic access to video streams based on interest.
In summary, IGMP facilitates efficient distribution of multicast video streams by managing group memberships, preserving bandwidth by directing streams only to interested receivers, and enabling open access to video content for any device on the LAN network that chooses to join a specific multicast group.

 EN
EN